30 June 2010
4 jam
4 jam
n. 2018
General relativity: Einstein’s insight

Starting in 1907, Einstein began trying to broaden special relativity to include gravity. His first breakthrough came when he was working in a patent office in Bern, Switzerland. “Suddenly a thought struck me,” he recalled. “If a man falls freely, he would not feel his weight… This simple thought experiment… led me to the theory of gravity.” He realised that there is a deep relationship between systems affected by gravity and ones that are accelerating.
Published in 1916, it explains that what we perceive as the force of gravity in fact arises from the curvature of space and time.
Einstein proposed that objects such as the sun and the Earth change this geometry.
Simple Relativity - Understanding Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity https://youtu.be/TgH9KXEQ0YU via @YouTube
Instant Expert: General relativity | New Scientist
https://www.newscientist.com/round-up/instant-expert-general-relativity/
People also ask
How did Einstein come up with the theory of general relativity?
General relativity (GR) is a theory of gravitation that was developed by Albert Einstein between 1907 and 1915, with contributions by many others after 1915.
maw 30 dec. 2017
The formula for determining time dilation
in special relativity is: Thus the duration of the clock cycle of a
moving clock is found to be increased: it is measured to be "running
slow". ... Time dilation of magnitude corresponding to this (Lorentz) factor has been experimentally confirmed, as described below.
Time dilation - Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_dilation
The formula for determining time dilation in special relativity is: Thus the duration of the clock cycle of a moving clock is found to be increased: it is measured to be "running slow". ... Time dilation of magnitude corresponding to this (Lorentz) factor has been experimentally confirmed, as described below
The formula for determining time dilation in special relativity is: Thus the duration of the clock cycle of a moving clock is found to be increased: it is measured to be "running slow". ... Time dilation of magnitude corresponding to this (Lorentz) factor has been experimentally confirmed, as described below
Length Contraction

|
IndexRelativity concepts | ||||
|
Go Back |
Time Dilation
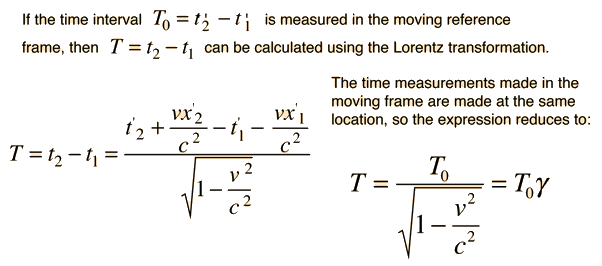  See also Gravitational time dilation
|
Index Relativity concepts | ||||
|
Go Back |
"Relativistic Mass"The increase in "effective mass" with speed is given by the expression It follows from the Lorentz transformation when collisions are described from a fixed and moving reference frame, where it arises as a result of conservation of momentum. You can also approach it from the relativistic energy expression  The increase in relativistic "effective mass" is associated with speed of light c the speed limit of the universe. This increased effective mass is evident in cyclotrons and other accelerators where the speed approaches c. Exploring the calculation above will show that you have to reach 14% of the speed of light, or about 42 million m/s before you change the effective mass by 1%. This language about "effective mass" is included here because it has long been used in elementary textbooks to describe the increase in energy with velocity, and it has a certain appeal for the description of relativistic effects such as the Cambridge example. But you won't find it in modern physics textbooks. One comment from a classic work on relativity is "Ouch! The concept of 'relativistic mass' is subject to misunderstanding. That's why we don't use it. First, it applies the name mass - belonging to the magnitude of a 4- vector - to a very different concept, the time component of a 4-vector. Second, it makes increase of energy of an object with velocity or momentum appear to be connected with some change in internal structure of the object. In reality, the increase of energy with velocity originates not in the object but in the geometric properties of space-time itself." (Taylor and Wheeler in Spacetime Physics)
|
Index Relativity concepts | |||
|
Go Back |
"Relativistic Mass" ExampleAt the electron accelerator in Cambridge, Mass., the final acceleration stage has the following characteristics:
Problems with variable mass concept |
Index Relativity concepts Reference Zukav | ||||||||||||
|
Go Back |
Problems with variable massEven though circumstances like that described at the Cambridge accelerator are conveniently described by assuming an increasing mass, that is not the only way to describe these experiments, and there are problems with the concept of variable relativistic mass. Einstein's point of view is described in the following quote:
|
Index Relativity concepts | ||
|
Go Back |
The Postulates of Special Relativity
https://www.nobelprize.org/educational/physics/relativity/postulates-1.html
People also ask
What is special theory of relativity?



No comments:
Post a Comment