Transient response
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transient_response
Transient response
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaThis article's factual accuracy is disputed. (June 2009) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) 
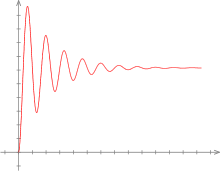
This article needs attention from an expert in Engineering. (June 2009) In electrical engineering and mechanical engineering, a transient response or natural response is the response of a system to a change from an equilibrium or a steady state. The transient response is not necessarily tied to "on/off" events but to any event that affects the equilibrium of the system. The impulse response and step response are transient responses to a specific input (an impulse and a step, respectively).Damping oscillation is a typical transient response, where the output value oscillates until finally reaching a steady-state value (The underdamped response case).
Contents
Damping
The response can be classified as one of three types of damping that describes the output in relation to the steady-state response.
An underdamped response is one that oscillates within a decaying envelope. The more underdamped the system, the more oscillations and longer it takes to reach steady-state. Here damping ratio is always <2.
A critically damped response is that response that reaches the steady-state value the fastest without being underdamped. It is related to critical points in the sense that it straddles the boundary of underdamped and overdamped responses. Here, damping ratio is always equal to one. There should be no oscillation about the steady state value in the ideal case.
An overdamped response is the response that does not oscillate about the steady-state value but takes longer to reach than the critically damped case. Here damping ratio is >1 it is the response of a system with respect to the input as a function of time
Properties
Typical second order transient system properties- Rise time
- Rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value. Typically, these values are 10% and 90% of the step height.
- Overshoot
- Overshoot is when a signal or function exceeds its target. It is often associated with ringing.
- Settling time
- Settling time is the time elapsed from the application of an ideal instantaneous step input to the time at which the output has entered and remained within a specified error band.
- Delay-time
- The delay time is the time required for the response to reach half the final value the very first time.[1]
- Peak time
- The peak time is the time required for the response to reach the first peak of the overshoot.[1]
- Steady-state error
- 2003's Instrument Engineers' Handbook defines the steady-state error of a system as "the difference between the desired final output and the actual one" when the system reaches a steady state, when its behavior may be expected to continue if the system is undisturbed.[2]
See also
References
- Ogata, Katsuhiko. Modern Control Engineering (4 ed.). Prentice-Hall. p. 230. ISBN 0-13-043245-8.
In control engineering, a state-space representation is a mathematical model of a physical system as a set of input, output and state variables related by first-order differential equations. "State space" refers to the space in which the variables on the axes are the state variables.
State-space representation - Wikipedia
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/State-space_representation
People also ask
What is a state in artificial intelligence?

No comments:
Post a Comment